The science behind building the most iconic weapon
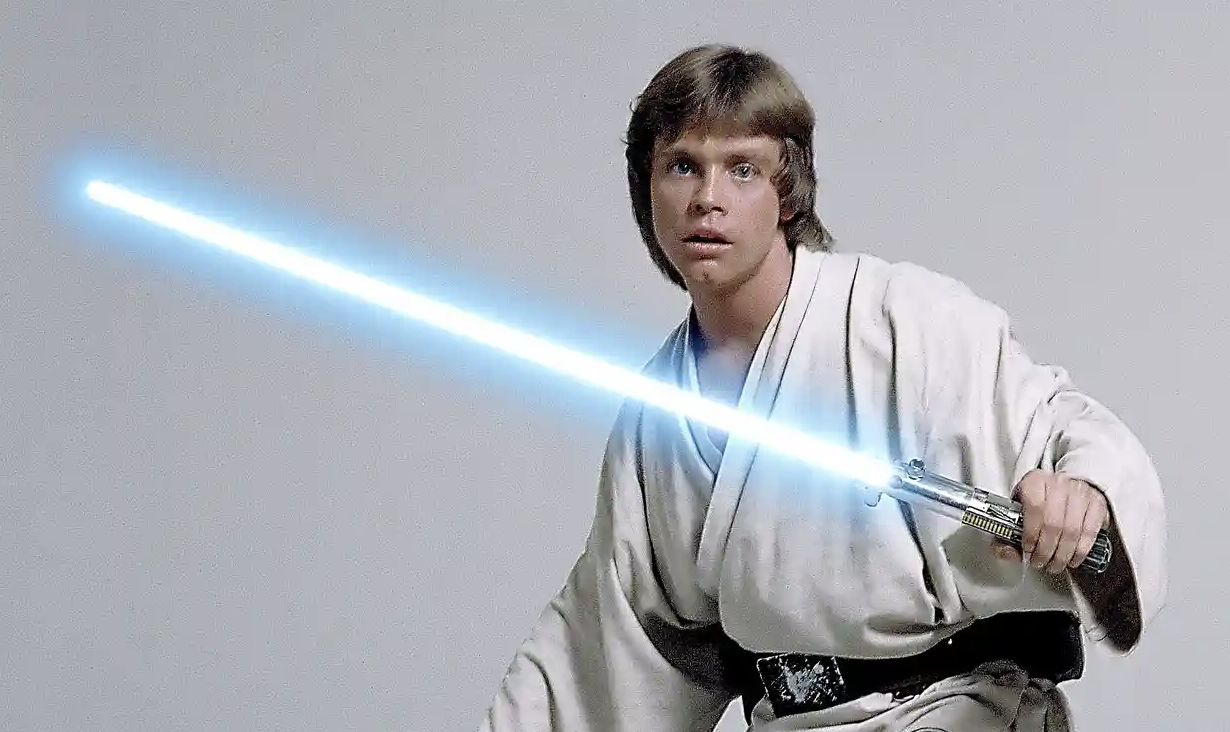
Of all the Sci-Fi weapons, the lightsaber is the most recognized. The whirring, glowing, and powerful lightsabers of the Star Wars universe are staples of Sci-Fi and beloved by many. The brightly colored blades were introduced to the masses by George Lucas’ Star Wars: A New Hope, where the Jedi Knights wield these flashy swords. In the past few years, geniuses at a popular YouTube channel called Hacksmith Industries have been able to recreate the fiery beam of a lightsaber. So how do these replicas compare to the ones depicted in the films?
In the movies, assembling a lightsaber is the first test of a Jedi. They must assemble the hilt which is made out of metal and can be customized. Once the hilt is made the Jedi must find and insert the Kyber Crystal which gives the blade color (1).
In reality, there aren’t Kyber crystals and Jedi Knights, so when constructing the first fully functional lightsaber Hackersmith technologies used plasma. Plasma is the fourth state of matter, a superheated gas that begins to separate the electrons from their atoms (2). Engineers spent months formulating the optimal mix of oxygen and liquid propane gas to create a blade that big out of plasma (3). When lit, this super oxygen-rich gas can reach the temperatures needed to transform the gas into a solid-looking mass of atoms that are so hot their electrons separate. The blade reaches temperatures higher than 4,000° degrees Fahrenheit, making melting through steel easy. For context, the metal with the highest melting point is Tungsten which has a melting point of 3,399°C (4). To control this hot plasma, the engineers designed a nozzle that creates a laminar flow of the gasses, which is the flow of a substance through space where both the direction of flow and the velocity are the same (5). An example of this property is in your veins: your blood flows throughout your body steadily. The nozzle that they designed allowed them to make a neat edge to the blade and far less spread of the flame.
With some clever engineering and the universal love for the brightly colored blades of Star Wars, Hacksmith Industries created a functional lightsaber, one so hot it can melt through steel like butter, formed using science and some extremely hot gasses. This ongoing project to build a perfect lightsaber is a testament to how much this one Sci-Fi weapon spread into the hearts of many to live out the childhood dream of becoming a Jedi and wielding a lightsaber.
Bibliography
1. (n.d.). Kyber Crystal (Lightsaber Crystal). StarWars.com. Retrieved from https://www.starwars.com/databank/lightsaber-crystal.
2. (2020) Plasma Science and Fusion Center. What is Plasma? Mit.edu. Retrieved from https://www.psfc.mit.edu/vision/what_is_plasma.
3. (n.d.). . Lightsabers. Www.hacksmith.com. Retrieved from https://www.hacksmith.com/projects/lightsabers.
4. (n.d.). A Guide to Metal Melting Points. NeoNickel. Retrieved from https://www.neonickel.com/technical-resources/general-technical-resources/a-guide-to-metal-melting-points/#:~:text=Tungsten%20is%20the%20highest%20melting.
5. The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (2019). Laminar flow. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved from https://www.britannica.com/science/laminar-flow.
Images




Comments are closed.