Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun’s discovery of microRNAs reshaped the field of genetics and earned them the 2024 Nobel Prize.
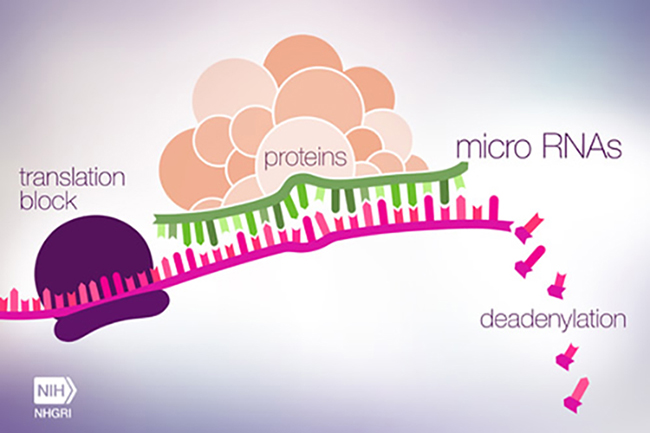
In 1993, Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun discovered microRNAs (miRNAs) while studying the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Caenorhabditis elegans are 1mm long multicellular organisms that live in temperate soil environments. They were the first multicellular organisms to have their entire genome sequenced. (1) There are two types of RNA molecules: non-coding RNA and messenger RNA. Messenger RNA serves as a template for protein production inside a cell. Non-coding RNA is RNA that does not code for proteins but has other important cell regulation functions, and microRNA falls under this umbrella. While miRNAs do not code for proteins, they regulate gene expression. (2) Their research reveals how miRNAs bind to mRNA to inhibit protein synthesis, which changes how cells develop and function.
MicroRNA in action controlling the expression of a gene.
Ambros and Ruvkuns’ research illustrated that miRNAs are essential for properly timing developmental events in organisms. They found that miRNAs are conserved across species and have a fundamental role in biology. This conservation of miRNAs shows their importance in many processes, including cell differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. Each cell starts as a generic stem-like cell and is then matured into a specialized cell inside the human body through cell differentiation. (3) Proliferation is when cells increase in size and number through cell division. (4) Apoptosis is programmed cell death, a process by which the body removes unnecessary or abnormal cells. (5) Since a failure of apoptosis, proliferation, or cell differentiation are all prerequisites for cancer and other diseases, the scientists’ discovery of the dysregulation of miRNA is essential. Understanding miRNA pathways offers potential treatments to modulate gene expression in people with diseases. (6)
Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun were awarded the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology for their work. Born in 1953, Victor Ambros is a professor at UMass Chan Medical School. He completed his undergraduate and doctoral studies at MIT. Gary Ruvkun, born in 1952, is a professor of genetics at Harvard Medical School. He earned his Ph.D. from Harvard. Their began collaborating when they were postdoc researchers in Robert Horvits’s lab at MIT, studying the development of C. elegans. (7)
Ambros and Ruvkun’s research focuses on understanding how gene expression is regulated during the development of C. elegans. Their first discovery was the miRNA, lin-4, which regulates the timing of larvae development by repressing the expression of the lin-14 gene. (6) In simpler terms, the lin-14 and lin-4 genes control when different parts of the larva develop at certain times in their maturation. DNA has two strands running antiparallel to each other. mRNA has only one and relies on the cell to complete the other side. Lin-4 can prevent lin-14’s translation to protein by binding to complementary sequences on the untranslated regions of lin-14 mRNA. (6) This mechanism happens in every species, including humans.
Scientists are exploring how miRNAs can be biomarkers for various diseases and be used as tumor suppressors, making them targets for cancer treatments. Also, miRNAs have been studied as biomarkers for disease diagnosis and prognosis because their expression levels can reveal health information. Ambros and Ruvkun’s research has significantly advanced the field of genetics and also has formed a base for future cancer treatments.
Citations:
- What is Caenorhabditis elegans and why work on it? – Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC) – College of Biological Sciences. (2025). Umn.edu.
Retrieved from
https://cgc.umn.edu/what-is-c-elegans
- Harvard Medical School Scientist Gary Ruvkun Receives Nobel Prize for Discovery of microRNA. (2024, October 7). Harvard.edu.
Retrieved from https://hms.harvard.edu/news/harvard-medical-school-scientist-gary-ruvkun-receives-nobel-prize-discovery-microrna?utm_source - NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. (2025). Cancer.gov. https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/cell-differentiation
- NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. (2025). Cancer.gov.
Retrieved from
- NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. (2025). Cancer.gov.
Retrieved from https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/apoptosis
- Trafton, A. (2024, October). Victor Ambros ’75, PhD ’79 and Gary Ruvkun share Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Retrieved from:
- The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2024. (2024). NobelPrize.org.
Retrieved from: https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/2024/press-release/?utm_source
Images:
Staff, G. (2016, April 27). MicroRNA Expression Could Be Key to Leukemia Treatment. GEN – Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology News.
Retrieved from:







Comments are closed.